
The plane of a face-centered cubic lattice is a hexagonal grid.Īttempting to create a base-centered cubic lattice (i.e., putting an extra lattice point in the center of each horizontal face) results in a simple tetragonal Bravais lattice.Ĭoordination number (CN) is the number of nearest neighbors of a central atom in the structure. The face-centered cubic lattice is closely related to the hexagonal close packed (hcp) system, where two systems differ only in the relative placements of their hexagonal layers.
#Nacl lattice structure plus
The face-centered cubic lattice (cF) has lattice points on the faces of the cube, that each gives exactly one half contribution, in addition to the corner lattice points, giving a total of 4 lattice points per unit cell ( 1⁄ 8 × 8 from the corners plus 1⁄ 2 × 6 from the faces). It has a net total of two lattice points per unit cell ( 1⁄ 8 × 8 + 1). The body-centered cubic lattice (cI) has one lattice point in the center of the unit cell in addition to the eight corner points. Each atom at a lattice point is then shared equally between eight adjacent cubes, and the unit cell therefore contains in total one atom ( 1⁄ 8 × 8). The primitive cubic lattice (cP) consists of one lattice point on each corner of the cube this means each simple cubic unit cell has in total one lattice point. The three Bravais lattices in the cubic crystal system are: Although the unit cells in these crystals are conventionally taken to be cubes, the primitive unit cells often are not. the diamond and the zincblende lattices are fcc but not close-packed.Įach is subdivided into other variants listed below. However, fcc stands for a face-centered-cubic Bravais lattice, which is not necessarily close-packed when a motif is set onto the lattice points. Note: the term fcc is often used in synonym for the cubic close-packed or ccp structure occurring in metals.

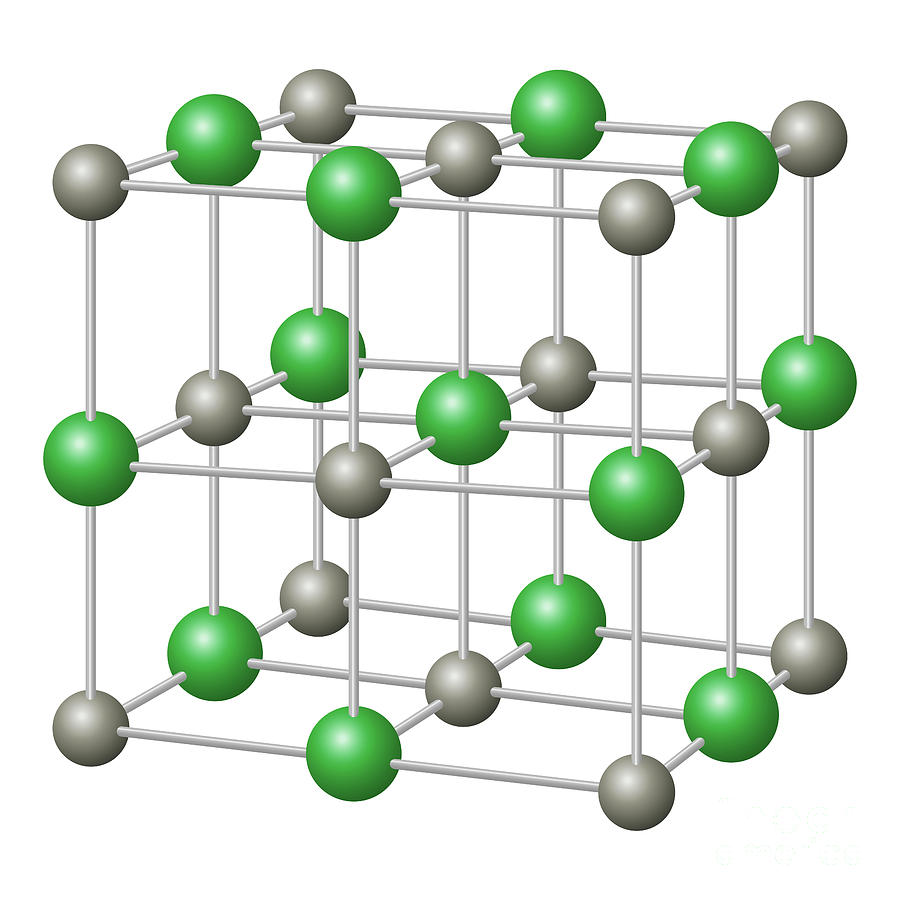
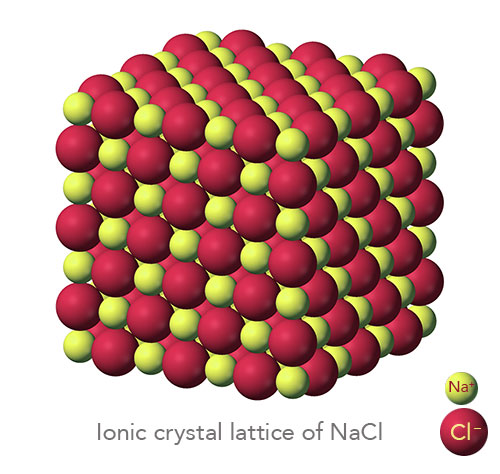
Since NaCl is an ionic structure and cations are smaller than anions it is assumed that radius of cation = r c and the radius of an anion = r A. Hence number of molecule / unit cell = 4. Since there are 4 Na + ions and four Cl ions in a NaCl unit cell, there are four NaCl molecule present in a unit cell. There is one whole Cl ion at the centre of the structure. Hence every edge lattice point carries ¼ of an atom. Every edge lattice points is shared by four neighbouring unit cell. Hence total number of Na +ions = 4Ĭalculation for Cl = There are 12 Cl ions at the edges. The face of such a unit cell is shown.Ĭalculation for Na + = Here Na + forms a FCC structure. A face of this unit cell is shown.Īnother NaCl unit cell can be considered with the positions of Na + and Cl ions interchanged. NaCl unit cell with Na + ions occupying the regular FCC lattice points with Cl ions positioned at alternate points. It is a combination of two FCC sublattice one made up of Na +ions and the other of Cl ions as if one sublattice is translated through the other along the cube edges. This is an ionic structure in which the Na +ions and Cl


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
